Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma
KEYTRUDA, in combination with LENVIMA, is indicated for the first-line treatment of adult patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
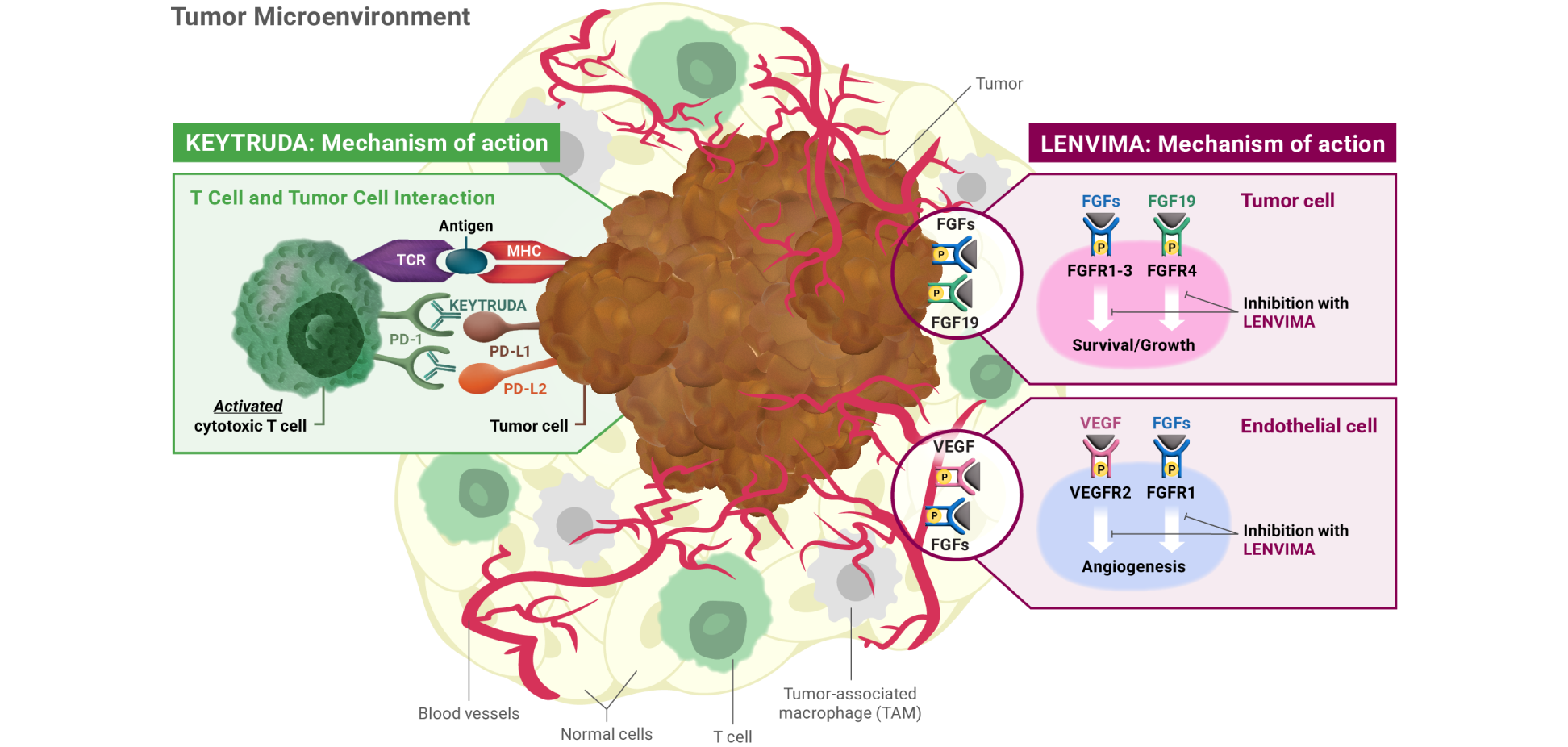
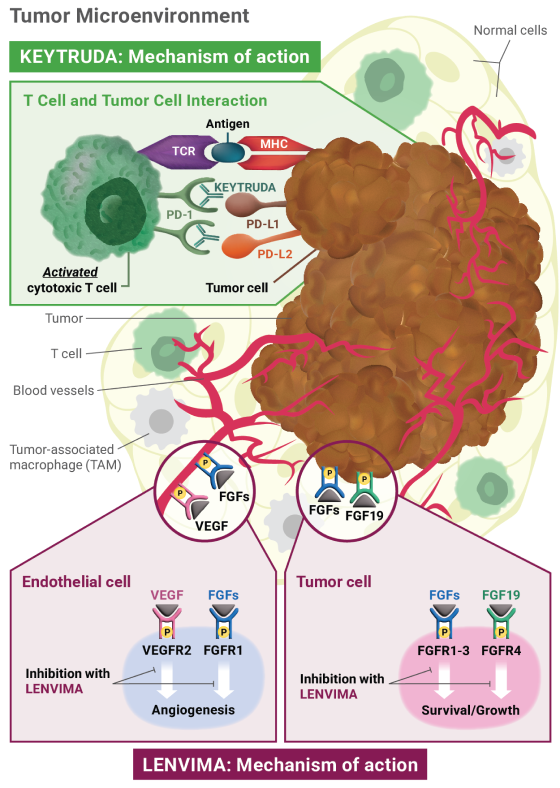
Mechanism of action: KEYTRUDA
KEYTRUDA is a humanized monoclonal antibody that binds to the PD-1 receptor, blocking both immune-suppressing ligands, PD-L1 and PD-L2, from interacting with PD-1 to help restore T-cell response and immune response. Restoring active T-cell response could affect both normal healthy cells and tumor cells.


Mechanism of action: LENVIMA
LENVIMA is thought to block receptors required for tumor growth and blood vessel development.
FGF = fibroblast growth factor; FGFR = fibroblast growth factor receptor; FLT = Fms-related tyrosine kinase; KDR = kinase insert domain receptor; KIT = receptor tyrosine kinase; MHC = major histocompatibility complex; PD-1 = programmed death receptor-1; PDGFRA = platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha; PD-L1 = programmed death ligand 1; PD-L2 = programmed death ligand 2; RET = rearranged during transfection; TCR = T-cell receptor; TKI = tyrosine kinase inhibitor; VEGF = vascular endothelial growth factor; VEGFR1 (FLT1) = vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 (FLT1); VEGFR2 (KDR) = vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (KDR); VEGFR3 (FLT4) = vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 (FLT4).
Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma
KEYTRUDA, in combination with LENVIMA, is indicated for the first-line treatment of adult patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
Advanced Endometrial Carcinoma
KEYTRUDA, in combination with LENVIMA, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with advanced endometrial carcinoma that is mismatch repair proficient (pMMR) as determined by an FDA-approved test or not microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H), who have disease progression following prior systemic therapy in any setting and are not candidates for curative surgery or radiation.
Severe and Fatal Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions
Immune-Mediated Pneumonitis
Immune-Mediated Colitis
Hepatotoxicity and Immune-Mediated Hepatitis
KEYTRUDA as a Single Agent
Immune-Mediated Endocrinopathies
Adrenal Insufficiency
Hypophysitis
Thyroid Disorders
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (DM), Which Can Present With Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Immune-Mediated Nephritis With Renal Dysfunction
Immune-Mediated Dermatologic Adverse Reactions
Other Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions
Infusion-Related Reactions
Complications of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (HSCT)
Increased Mortality in Patients With Multiple Myeloma
Embryofetal Toxicity
Adverse Reactions
Lactation
Hypertension
Cardiac Dysfunction
Arterial Thromboembolic Events
Hepatotoxicity
Renal Failure or Impairment
Proteinuria
Diarrhea
Fistula Formation and Gastrointestinal Perforation
QT Interval Prolongation
Hypocalcemia
Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome (RPLS)
Hemorrhagic Events
Impairment of Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Suppression/Thyroid Dysfunction
Impaired Wound Healing
Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (ONJ)
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Adverse Reactions
Use in Specific Populations
KEYTRUDA, in combination with LENVIMA, is indicated for the first-line treatment of adult patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
KEYTRUDA, in combination with LENVIMA, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with advanced endometrial carcinoma that is mismatch repair proficient (pMMR) as determined by an FDA-approved test or not microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H), who have disease progression following prior systemic therapy in any setting and are not candidates for curative surgery or radiation.
Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma
KEYTRUDA, in combination with LENVIMA, is indicated for the first-line treatment of adult patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
Advanced Endometrial Carcinoma
KEYTRUDA, in combination with LENVIMA, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with advanced endometrial carcinoma that is mismatch repair proficient (pMMR) as determined by an FDA-approved test or not microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H), who have disease progression following prior systemic therapy in any setting and are not candidates for curative surgery or radiation.
Severe and Fatal Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions: KEYTRUDA is a monoclonal antibody that belongs to a class of drugs that bind to either the programmed death receptor-1 (PD-1) or the programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1), blocking the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway, thereby removing inhibition of the immune response, potentially breaking peripheral tolerance and inducing immune-mediated adverse reactions. Immune-mediated adverse reactions, which may be severe or fatal, can occur in any organ system or tissue, can affect more than one body system simultaneously, and can occur at any time after starting treatment or after discontinuation of treatment. Important immune-mediated adverse reactions listed here may not include all possible severe and fatal immune-mediated adverse reactions.
Hypertension: In differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC), hypertension occurred in 73% of patients on LENVIMA (44% grade 3-4). In advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC), hypertension occurred in 42% of patients on LENVIMA + everolimus (13% grade 3). Systolic blood pressure ≥160 mmHg occurred in 29% of patients, and 21% had diastolic blood pressure ≥100 mmHg. In unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), hypertension occurred in 45% of LENVIMA-treated patients (24% grade 3). Grade 4 hypertension was not reported in HCC.
Severe and Fatal Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions
Immune-Mediated Pneumonitis
Immune-Mediated Colitis
Hepatotoxicity and Immune-Mediated Hepatitis
KEYTRUDA as a Single Agent
Immune-Mediated Endocrinopathies
Adrenal Insufficiency
Hypophysitis
Thyroid Disorders
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (DM), Which Can Present With Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Immune-Mediated Nephritis With Renal Dysfunction
Immune-Mediated Dermatologic Adverse Reactions
Other Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions
Infusion-Related Reactions
Complications of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (HSCT)
Increased Mortality in Patients With Multiple Myeloma
Embryofetal Toxicity
Adverse Reactions
Lactation
Hypertension
Cardiac Dysfunction
Arterial Thromboembolic Events
Hepatotoxicity
Renal Failure or Impairment
Proteinuria
Diarrhea
Fistula Formation and Gastrointestinal Perforation
QT Interval Prolongation
Hypocalcemia
Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome (RPLS)
Hemorrhagic Events
Impairment of Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Suppression/Thyroid Dysfunction
Impaired Wound Healing
Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (ONJ)
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Adverse Reactions
Use in Specific Populations
Severe and Fatal Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions: KEYTRUDA is a monoclonal antibody that belongs to a class of drugs that bind to either the programmed death receptor-1 (PD-1) or the programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1), blocking the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway, thereby removing inhibition of the immune response, potentially breaking peripheral tolerance and inducing immune-mediated adverse reactions. Immune-mediated adverse reactions, which may be severe or fatal, can occur in any organ system or tissue, can affect more than one body system simultaneously, and can occur at any time after starting treatment or after discontinuation of treatment. Important immune-mediated adverse reactions listed here may not include all possible severe and fatal immune-mediated adverse reactions.
Severe and Fatal Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions
Immune-Mediated Pneumonitis
Immune-Mediated Colitis
Hepatotoxicity and Immune-Mediated Hepatitis
KEYTRUDA as a Single Agent
Immune-Mediated Endocrinopathies
Adrenal Insufficiency
Hypophysitis
Thyroid Disorders
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (DM), Which Can Present With Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Immune-Mediated Nephritis With Renal Dysfunction
Immune-Mediated Dermatologic Adverse Reactions
Other Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions
Infusion-Related Reactions
Complications of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (HSCT)
Increased Mortality in Patients With Multiple Myeloma
Embryofetal Toxicity
Adverse Reactions
Lactation
Hypertension: In differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC), hypertension occurred in 73% of patients on LENVIMA (44% grade 3-4). In advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC), hypertension occurred in 42% of patients on LENVIMA + everolimus (13% grade 3). Systolic blood pressure ≥160 mmHg occurred in 29% of patients, and 21% had diastolic blood pressure ≥100 mmHg. In unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), hypertension occurred in 45% of LENVIMA-treated patients (24% grade 3). Grade 4 hypertension was not reported in HCC.
Hypertension
Cardiac Dysfunction
Arterial Thromboembolic Events
Hepatotoxicity
Renal Failure or Impairment
Proteinuria
Diarrhea
Fistula Formation and Gastrointestinal Perforation
QT Interval Prolongation
Hypocalcemia
Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome (RPLS)
Hemorrhagic Events
Impairment of Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Suppression/Thyroid Dysfunction
Impaired Wound Healing
Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (ONJ)
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Adverse Reactions
Use in Specific Populations